Sometimes, it’s handy to be able to set up a quick environment for tests and also to take our Liquibase University certification courses. Here’s how to use Docker to create an MSSQL container.
1. Install the version of Liquibase you’d like to use.
2. Run MSSQL via Docker.
Use these instructions from Docker Hub. The instructions are not version specific.
- Run:
docker run -e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y' -e 'SA_PASSWORD=yourStrongPassword1$' -p 1433:1433 -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2017-CU8-ubuntu - Note, this will run with the tag
2017-CU8-ubuntu
3. Connect the database.
You can use SQLPlus or a SQL Browser. We used DBeaver. See the connection configuration below. The password will be what you specified in the -e SA_PASSWORD=yourStrongPassword1$ on docker image start in the previous section. From the above example, it would be: yourStrongPassword1$
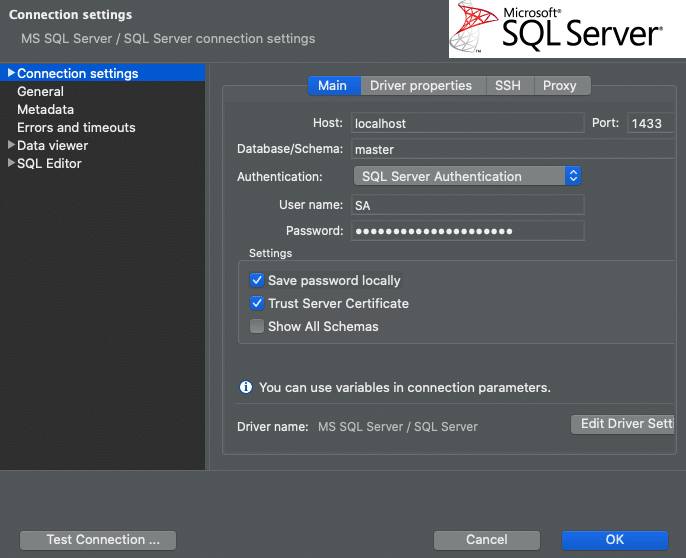
4. Prepare SQLServer with database/schemas/objects.
Now that we have a Docker container that is running MS SQLSERVER, we want to have a database with schemas to run Liquibase against. Or you can continue by using the default master db ; dbo schema.
5. Configure the Liquibase project.
You can use any Liquibase project you want. I use one I have committed to source:
- Make sure you are in the root of project folder (in this case, ronak_lb_projects)
- cd ronak_lb_projects/mssql
- verify liquibase.properties file has URL and passwords correct, mine looked like this:
# Enter the path for your changelog file. changeLogFile=changelog.sql # Enter the URL of the source database url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;database=master; # Enter the username for your source database. username: SA password: 'yourStrongPassword1$' driver=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver classpath: ../drivers/mssql-jdbc-8.2.2.jre8.jar #### Target Database Information #### ## The target database is the database you want to use to compare to your source database. logLevel: ERROR
You can test your configuration by running the liquibase updateSQL command.
liquibase --username=SA --password='yourStrongPassword1$' updateSQL
Destroy the Docker image
Find your container by listing it:
docker container ls -a
This command will return something like the following:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4d5674c2da35 mssql "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 days ago Up 2 days 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp some-sqlserver
Use the container ID to delete the image.
docker stop <containerid> docker container rm <containerid>


